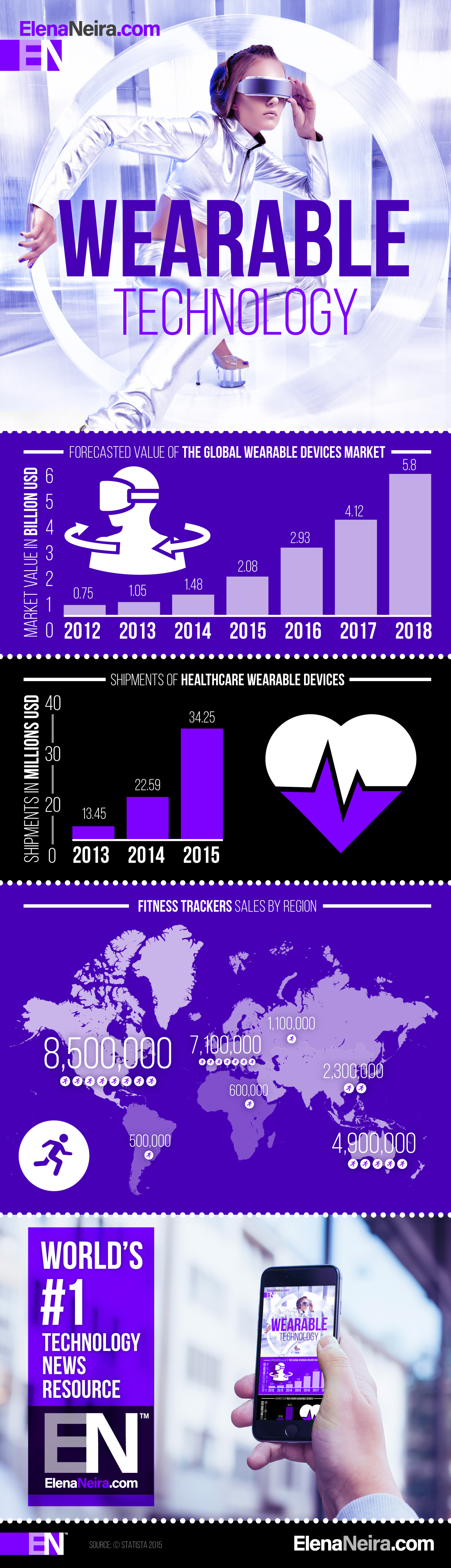
Today 3-D movie and video watching does go with strange-looking glasses. This does not have to be the case in the future if technologies like Automultiscopic Displays are brought to market. These new technologies that take glasses and any other “additional” hardware out of the user experience equation are particularly appealing in a mobile environment. If the user is moving around and has only a device such as a smartphone with him/her, how will 5G provide a 3-D experience?
Automultiscopic Displays on a Large-Scale: MIT’s Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Lab and the Weizmann Institute of Science demonstrate are reporting a prototype movie screen system called “Cinema 3D” that lets movie goes experience 3-D without wearing glasses, and does not require the high-resolution that other 3-D glass-free technologies require. The display technology that makes this possible is called automultiscopic display applied in a large-scale area. Cinema 3D “would use a series of lenses and mirrors to allow audiences to see the same 3-D (three dimensional) image from any seat in a theater.”
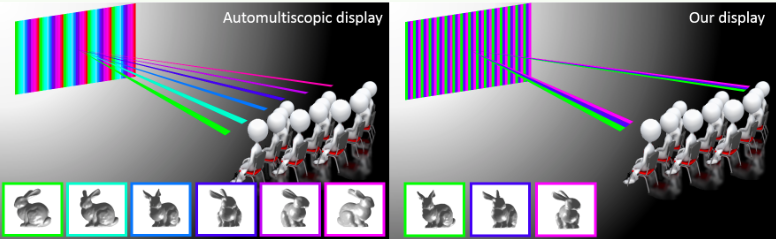
Aiming for real-world three-dimensional visual experiences: There is a very active 3-D imaging industry because users are interested in experiencing images and video that exhibit real-world-like properties. For TVs and movie screens, the technology for the future points at holographic imaging technologies which would present images that vary with varying perspectives. In the short term, solutions like this automultiscopic display could emerge if they present a compelling time-to-market cost effective picture.
@elenaneira
References: MIT News: A New 3-D Movie Screen Without The Glasses 3-D Cinema Large Automultiscopic Display