Happening in 5G, China’s decisive path to 5G continues and after recruiting Taiwan last month, this month Japan’s DoCoMo joins as participant in the IMT-2020(5G) Promotion Group Trial. Operator US Cellular reports 5G test results in the 15 GH band, and says it reached 9 Gbps up to 240 meters; NTIA delivers remarks on spectrum sharing with focus on 5G; ITU completes wireline enablers for 5G study; and interest in 5G continues to increase, Google trends reports a 10% uptake on Google searches for “5G” worldwide.
“Mobile Is a Shifting Landscape, Know the Terrain” – 5 Things Happening in 5G

China Adds DoCoMo to IMT-2020(5G) Promotion Group Trial
DoCoMo says that it has signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) with the China Academy of Information and Communication Technology (CAICT) to jointly investigate the standardization of 5G technologies and available frequency bands. CAICT is China’s national research organization in charge of policies and standardization strategies on information and communication in the country. Based on the MOU, DoCoMo will participate in the 5G Trial activities launched by the IMT-2020 (5G) Promotion Group which is CAICT’s initiative to verify 5G technologies, and to drive research and development to help standardize 5G. During the trial, DOCOMO and CAICT will also study a possible frequency bands for 5G networks. DoCoMo had joined the IMT-2020 (5G) Promotion Group in August-2016 to cooperate with major mobile providers and vendors on 5G R&D and standardization, including adding major options of 5G’s frequency bands as equipment and test specifications
Source: DoCoMo News Room

US Cellular 5G Trial in 15 GHz Reaches 9 Gbps
U.S. Cellular and Ericsson are reporting successful completion of 5G testing in the 15 GHz spectrum band which achieved peak throughput of 9 Gbps at a distance of 787 ft. (aprox. 240 meters) to bring the next-generation mobile network technology one step closer to deployment. Using this 15 GHz band, Ericsson installed 5G radios on a tower currently in commercial service. The over-the-air test was possible using an experimental FCC license. It run under varying environmental conditions to simulate real world use. The tests evaluated a number of new radio access (NX) carrier combinations to verify network throughput and performance benchmarks. The trials achieved peak throughput of 1.5Gbps at a distance of one mile and 9Gbps at a distance of 787 ft. The tests also included radio resource sharing, beamforming, beam tracking, peak throughput and multi-user MIMO tests. Michael S. Irizarry, Executive Vice President and Chief Technology Officer, U.S. Cellular,says: “This latest trial with Ericsson demonstrates incredible 9Gbps speeds in an environment that was close to a real world scenario, and we look forward to collaborating with Ericsson on the development of standards for a healthy 5G ecosystem. We are committed to giving our customers the best experience with the latest technology that can enhance their lives or businesses, and a fast, high-quality network that works whenever and wherever they need it.”
Source: US Cellular, Ericsson

Spectrum Sharing in Focus at NTIA
US NTIA Assistance Secretary Strickling delivers a ‘5G Wireless Future and the Role of the Federal Government’ remarks focusing on spectrum sharing efforts at the agency. He says that growth and innovation in the wireless sector will hinge in large part on the successful introduction of 5G networks and the ability to deliver the spectrum needed to power this and future generations of mobile technologies. More often than not, this spectrum has already being assigned to specific users such as the military and needs to be repurposed. From the outset, it has been clear to NTIA that in repurposing spectrum, the old method of clearing spectrum of federal users and then making it available for the exclusive use of commercial providers was no longer sustainable. Among new techniques that the agency has used is the “fast-track” which consists of a process to examine bands on an expedited basis as it was done for the AWS-3 auction and the FCC’s proceeding to quickly establish the Citizens Broadband Radio Service (CBRS) in the 3.5 GHz band. Beyond this example, NTIA’s strategy has been leading a fundamental shift in spectrum management that promotes and advances spectrum sharing among all users as a vital path forward to meeting the growing demand for additional spectrum for wireless technologies. Specifically affecting 5G networks, the NTIA has been looking at leveraging duplexing and spectrum usage schemes to promote co-existence of 5G federal and non-federal systems, and is also working on a more transparent and consistent process for determining interference criteria for effective sharing of spectrum. In closing remarks, Strickling also mentions that NTIA recognizes the need to more accurately quantify current spectrum demand, usage and projections of future requirements. “How granular does coverage need to be for emerging 5G applications? For IoT specifically? How important is reliability in an IoT environment? These are questions that will need to be considered in weighing future spectrum policy decisions.”
Source: US NTIA

ITU Completes Wireline Enablers for 5G Study
One of ITU’s IMT-2020/5G related activities in the last couple of years has been to host in ITU-R a preliminary study group looking into the networking innovations required to achieve the performance targets of 5G. The group met for a final time last December 7 to present their conclusions which highlighted as key themes new architecture, FMC (fixed-mobile convergence), network softwarization, and fronthaul/backhaul. As far as new architecture, a 3GPP-led core network evolution study showed 4 reference points important for the core: NG2 (reference point for the control plane between NextGen RAN and NextGen Core), NG3 (reference point for the user plane between NextGen RAN and NextGen Core), NG1 (reference point for the control plane between NextGen UE and NextGen Core), and NG6 (reference point between the NextGen Core and the data network). As far as FMC, it concluded that the approach has challenges like a lack of coherence among various protocols, lack of coherence among 4G, 5G, WLAN, Fixed BB Protocols, also a lack of coherence between user and control planes; in addition, a lack of coherence among identification types of different access technologies like (1) cellphone number for 4G/5G wireless access, (2) broadband ID for Fixed BB access, and (3) WLAN ID for WLAN access. As far as fronthaul/backhaul, Ethernet was the most talked about technology with both ROE (Radio Over Ethernet) and X-Ethernet presented solutions. As far as network softwarization, slicing and orchestration were big topics shown in several presentations including ETRI’s full system 28 GHz 5G proof-of-concepts at 2018 Winter Olympic Games. The study group’s output takes the form of five draft ITU international standards and four draft ITU technical reports to drive related work in ITU’s standardization expert groups.
Source: ITU

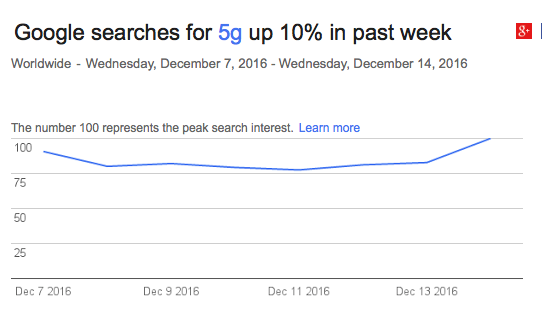
A 10% Increase WorldWide in Google Searches for “5G”
Google Trends reports that last week (December 7 – December 13, 2016) saw an uptake of 10% in Google searches for “5G” worldwide. Breaking it up by regions, the interest in the term increased the most in China (100%), India (41%) and South Korea (36%). Google also reports that the top related queries were ‘5G mobile’, ‘5G network’ and ‘5G wifi’
Image Source: Google Trends
Issue No. 8 (2016-12-20) of 5 Things Happening in 5G sifting through reliable sources to bring you carefully selected, buzzworthy, and focused biz, tech, and market trends.
Find us also in Facebook, Google+, Instagram, Medium, and Twitter. For partnerships, inquiries, please contact us at social media(at)5g-magazine.com.
© 2016 www.5g-magazine.com – All rights reserved. Use of this Web site signifies your agreement to its Terms & Conditions.